Convertire numeri in parole in Rupie Indiane e altre valute in Excel (Edizione 2025)
Ecco come convertire i numeri in parole in Rupie Indiane o in qualsiasi altra valuta in Excel.
Quando si lavora con documenti finanziari come fatture, preventivi, moduli fiscali, assegni o buoni di pagamento, è spesso necessario rappresentare i valori monetari sia in formato numerico che in parole scritte. Questo aggiunge un livello di professionalità e aiuta a prevenire frodi o fraintendimenti.
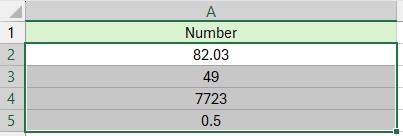
Esempio
Sebbene Microsoft Excel non abbia una funzionalità integrata per convertire numeri in parole, esistono più metodi efficaci per farlo: tramite VBA, funzioni LAMBDA o l'add-in Kutools per Excel.
Convertire Numeri in Parole in Rupie Indiane con VBA (Tutte le Versioni Microsoft)
- Convertire Numeri in Parole in Altre Valute (USD, EUR, ecc.)
- Salva la Cartella di Lavoro come File Abilitato per Macro
Convertire Numeri in Parole in Rupie Indiane con Funzione LAMBDA (Solo Microsoft 365)
Convertire Numeri in USD, EUR e Oltre 30 Altre Valute (Tutte le Versioni Microsoft)
Convertire Numeri in Parole in Rupie Indiane con VBA (Tutte le Versioni Microsoft)
Per gli utenti di qualsiasi versione di Excel, VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) offre un metodo personalizzabile per convertire importi numerici in parole utilizzando il sistema di numerazione indiano (es. migliaia, lakhs, crores).
Passo 1. Premere Alt + F11 per aprire l'editor VBA (finestra Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications).
Passo 2. Vai su Inserisci > Modulo.
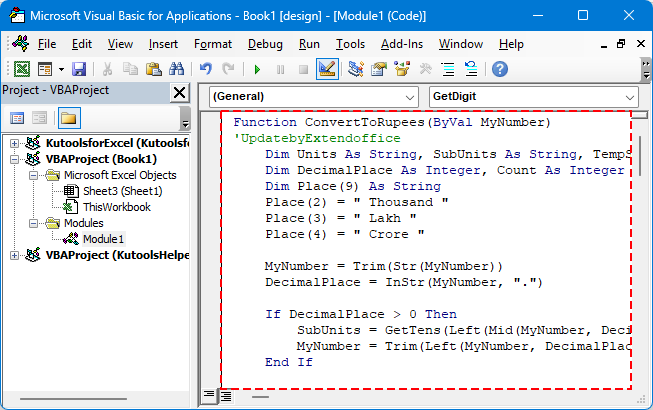
Passo 3. Incolla il codice VBA nel Modulo.
Convertire numeri in parole in Rupie Indiane
Function ConvertToRupees(ByVal MyNumber)
'UpdatebyExtendoffice
Dim Units As String, SubUnits As String, TempStr As String
Dim DecimalPlace As Integer, Count As Integer
Dim Place(9) As String
Place(2) = " Thousand "
Place(3) = " Lakh "
Place(4) = " Crore "
MyNumber = Trim(Str(MyNumber))
DecimalPlace = InStr(MyNumber, ".")
If DecimalPlace > 0 Then
SubUnits = GetTens(Left(Mid(MyNumber, DecimalPlace + 1) & "00", 2))
MyNumber = Trim(Left(MyNumber, DecimalPlace - 1))
End If
Count = 1
Do While MyNumber <> ""
TempStr = GetHundreds(Right(MyNumber, 3))
If TempStr <> "" Then Units = TempStr & Place(Count) & Units
If Len(MyNumber) > 3 Then
MyNumber = Left(MyNumber, Len(MyNumber) - 3)
Else
MyNumber = ""
End If
Count = Count + 1
Loop
ConvertToRupees = "Rupees " & Application.WorksheetFunction.Trim(Units)
If SubUnits <> "" Then
ConvertToRupees = ConvertToRupees & " and " & SubUnits & " Paise"
End If
ConvertToRupees = ConvertToRupees & " Only"
End Function
Private Function GetHundreds(ByVal MyNumber)
Dim Result As String
If Val(MyNumber) = 0 Then Exit Function
MyNumber = Right("000" & MyNumber, 3)
If Mid(MyNumber, 1, 1) <> "0" Then
Result = GetDigit(Mid(MyNumber, 1, 1)) & " Hundred "
End If
If Mid(MyNumber, 2, 1) <> "0" Then
Result = Result & GetTens(Mid(MyNumber, 2))
Else
Result = Result & GetDigit(Mid(MyNumber, 3))
End If
GetHundreds = Result
End Function
Private Function GetTens(TensText)
Dim Result As String
If Val(Left(TensText, 1)) = 1 Then
Select Case Val(TensText)
Case 10: Result = "Ten"
Case 11: Result = "Eleven"
Case 12: Result = "Twelve"
Case 13: Result = "Thirteen"
Case 14: Result = "Fourteen"
Case 15: Result = "Fifteen"
Case 16: Result = "Sixteen"
Case 17: Result = "Seventeen"
Case 18: Result = "Eighteen"
Case 19: Result = "Nineteen"
End Select
Else
Select Case Val(Left(TensText, 1))
Case 2: Result = "Twenty "
Case 3: Result = "Thirty "
Case 4: Result = "Forty "
Case 5: Result = "Fifty "
Case 6: Result = "Sixty "
Case 7: Result = "Seventy "
Case 8: Result = "Eighty "
Case 9: Result = "Ninety "
End Select
Result = Result & GetDigit(Right(TensText, 1))
End If
GetTens = Result
End Function
Private Function GetDigit(Digit)
Select Case Val(Digit)
Case 1: GetDigit = "One"
Case 2: GetDigit = "Two"
Case 3: GetDigit = "Three"
Case 4: GetDigit = "Four"
Case 5: GetDigit = "Five"
Case 6: GetDigit = "Six"
Case 7: GetDigit = "Seven"
Case 8: GetDigit = "Eight"
Case 9: GetDigit = "Nine"
Case Else: GetDigit = ""
End Select
End Function
Passo 4. Salva e torna a Excel.
Passo 5. Seleziona una cella e usa la formula in questo modo:
Premi il tasto Invio
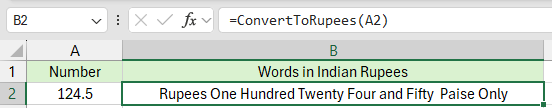
💡 Suggerimento: Questo metodo supporta i decimali (Paise) e funziona offline.
Limitazioni nell'uso di VBA
- Richiede di salvare la cartella di lavoro come file abilitato per macro (.xlsm).
- Le macro possono essere bloccate dalle impostazioni di sicurezza in alcuni ambienti.
Convertire Numeri in Parole in Altre Valute (USD, EUR, ecc.)
Per personalizzare l'output per altre valute, come "Dollari" o "Euro", puoi modificare i valori delle stringhe nella funzione VBA. Di seguito è riportata una versione semplificata e più flessibile della funzione.
Modello di Codice VBA Flessibile (Valuta Personalizzata)
'UpdatebyExtendoffice
Public Function NumberToWordsCustom(ByVal num As Double, Optional ByVal currency2 As String, Optional ByVal subCurrency As String) As String
Dim result As String
Dim dollars As Long
Dim cents As Long
dollars = Int(num)
cents = Round((num - dollars) * 100)
If Len(currency2) = 0 Then currency2 = "Dollars"
If Len(subCurrency) = 0 Then subCurrency = "Cents"
result = currency2 & " " & SpellNumber_English(dollars)
If cents > 0 Then
result = result & " and " & SpellNumber_English(cents) & " " & subCurrency
End If
NumberToWordsCustom = result & " Only"
End Function
Private Function SpellNumber_English(ByVal MyNumber As Long) As String
Dim Units As Variant, Tens As Variant, Teens As Variant
Dim Place() As String
Dim TempStr As String
Dim Count As Integer
Dim t As String
Dim StrNumber As String
Dim n As Integer
Place = Split(" Thousand Million Billion", " ")
Units = Array("", "One", "Two", "Three", "Four", "Five", "Six", "Seven", "Eight", "Nine")
Tens = Array("", "", "Twenty", "Thirty", "Forty", "Fifty", "Sixty", "Seventy", "Eighty", "Ninety")
Teens = Array("Ten", "Eleven", "Twelve", "Thirteen", "Fourteen", "Fifteen", "Sixteen", "Seventeen", "Eighteen", "Nineteen")
StrNumber = Trim(Str(MyNumber))
Count = 0
Do While StrNumber <> ""
n = Val(Right(StrNumber, 3))
If n <> 0 Then
t = ConvertHundreds(n, Units, Tens, Teens)
If Count > 0 Then t = t & " " & Place(Count - 1)
TempStr = t & " " & TempStr
End If
If Len(StrNumber) > 3 Then
StrNumber = Left(StrNumber, Len(StrNumber) - 3)
Else
StrNumber = ""
End If
Count = Count + 1
Loop
SpellNumber_English = Trim(TempStr)
End Function
Private Function ConvertHundreds(ByVal n As Integer, Units As Variant, Tens As Variant, Teens As Variant) As String
Dim result As String
If n >= 100 Then
result = Units(Int(n / 100)) & " Hundred "
n = n Mod 100
End If
If n >= 20 Then
result = result & Tens(Int(n / 10)) & " "
n = n Mod 10
ElseIf n >= 10 Then
result = result & Teens(n - 10) & " "
n = 0
End If
If n > 0 Then
result = result & Units(n)
End If
ConvertHundreds = Trim(result)
End Function
Formula VBA Esempio:
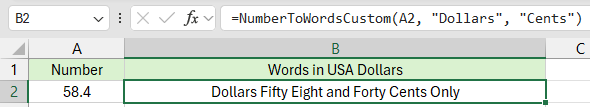
Formula VBA Esempio di Altra Valuta:
=NumberToWordsCustom(A2, "Euro", "Centesimi")
=NumberToWordsCustom(A2, "Sterline", "Pence")
Il codice è flessibile—basta passare la valuta e la sottounità desiderata.
Salva la Cartella di Lavoro come File Abilitato per Macro
Se stai usando VBA, è fondamentale salvare la cartella di lavoro con le macro abilitate. Altrimenti, il tuo codice andrà perso quando il file verrà chiuso.
Passo 1. Vai su File > Salva con nome
Passo 2. Seleziona una posizione e scegli il tipo di file: Cartella di Lavoro Excel Abilitata per Macro (*.xlsm).
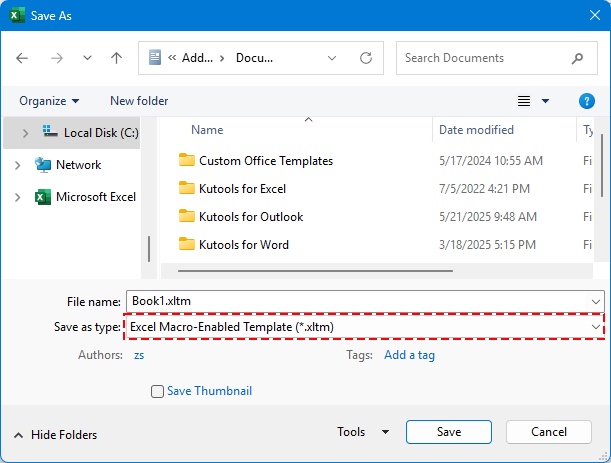
Passo 3. Clicca Salva.
✅ Le tue funzioni personalizzate come =ConvertToRupees(A2) ora persistono e possono essere riutilizzate in qualsiasi momento.
Convertire Numeri in Parole in Rupie Indiane con Funzione LAMBDA (Solo Microsoft 365)
Per gli utenti di Excel 365, puoi usare LAMBDA, una nuova funzionalità di Excel che ti permette di definire formule personalizzate—senza bisogno di VBA.
🪄 Cos'è LAMBDA?
LAMBDA è una funzionalità in Excel che ti consente di creare le tue funzioni personalizzate utilizzando formule—proprio come le funzioni integrate come SOMMA o SE, ma senza bisogno di alcun codice o macro. È ottimo per semplificare logiche ripetitive e rendere i tuoi fogli di calcolo più puliti e facili da mantenere.
Passo 1: Vai al Gestore Nomi e clicca Formule > Gestore Nomi.
Passo 2: Crea un nuovo Nome.
Clicca sul pulsante Nuovo.
Inserisci un Nome.
Esempio: RupeeToWords
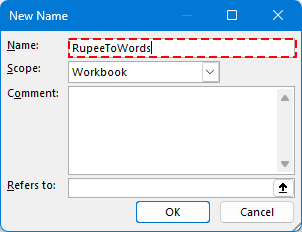
Passo 3: Incolla questa formula LAMBDA nel campo Si riferisce a:
=LAMBDA(n, LET( units, {"","Uno","Due","Tre","Quattro","Cinque","Sei","Sette","Otto","Nove"}, teens, {"Dieci","Undici","Dodici","Tredici","Quattordici","Quindici","Sedici","Diciassette","Diciotto","Diciannove"}, tens, {"","","Venti","Trenta","Quaranta","Cinquanta","Sessanta","Settanta","Ottanta","Novanta"}, num, INT(n), paise, ROUND((n - INT(n)) * 100, 0), ConvertTwo, LAMBDA(x, IF(x<10, INDEX(units, x+1), IF(x<20, INDEX(teens, x-9), INDEX(tens, INT(x/10)+1) & IF(MOD(x,10)>0, " " & INDEX(units, MOD(x,10)+1), "") ) ) ), ConvertThree, LAMBDA(x, IF(x=0, "", IF(x<100, ConvertTwo(x), INDEX(units, INT(x/100)+1) & " Cento" & IF(MOD(x,100)>0, " " & ConvertTwo(MOD(x,100)), "") ) ) ), words, IF(num=0, "Zero", TEXTJOIN(" ", TRUE, IF(INT(num/10000000)>0, ConvertTwo(INT(num/10000000)) & " Crore", ""), IF(MOD(INT(num/100000),100)>0, ConvertTwo(INT(MOD(num,10000000)/100000)) & " Lakh", ""), IF(MOD(INT(num/1000),100)>0, ConvertTwo(INT(MOD(num,100000)/1000)) & " Mille", ""), IF(MOD(INT(num/100),10)>0, INDEX(units, INT(MOD(num,1000)/100)+1) & " Cento", ""), IF(MOD(num,100)>0, ConvertTwo(MOD(num,100)), "") ) ), result, "Rupie " & words & IF(paise>0, " e " & ConvertTwo(paise) & " Paise", "") & " Solamente", result ))Clicca OK per salvare il nuovo Nome.
Passo 3. Chiudi il Gestore Nomi e torna a Excel.
Passo 4. Usa la formula in qualsiasi cella in questo modo:
Premi il tasto Invio.
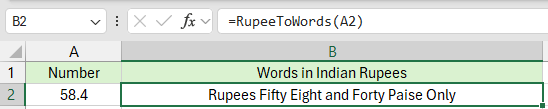
👀 Il codice completo della funzione LAMBDA gestisce Crore, Lakh, Migliaia e decimali.
Convertire Numeri in USD, EUR e Oltre 30 Altre Valute (Tutte le Versioni Microsoft)
Per la soluzione più efficiente e professionale, usa Kutools per Excel's Numbers to Words. Questo potente strumento supporta:
🌍 Oltre 30 valute, tra cui:
- Dollari USA (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- Yuan Cinese (CNY)
- Sterline Britanniche (GBP)
- ecc.
Passo 1. Seleziona le celle che vuoi convertire.
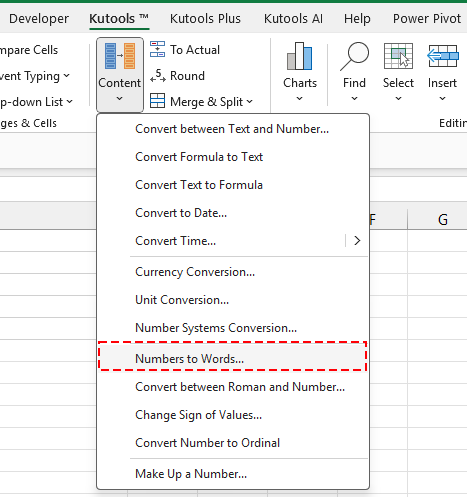
Passo 2. Vai su Kutools > Testo > Numbers to Words
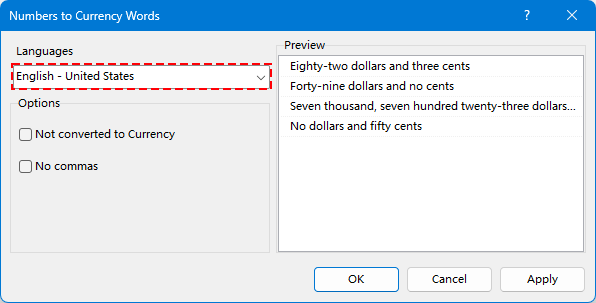
Passo 3. Scegli la tua valuta di destinazione e clicca OK.
I numeri vengono convertiti nella valuta specificata.
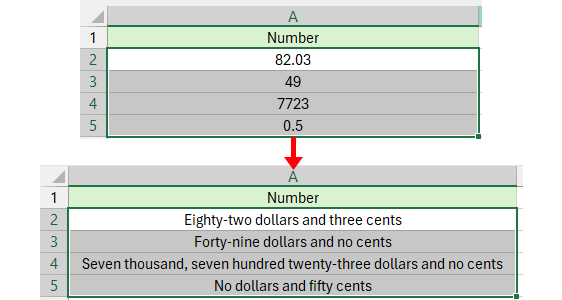
😁 Suggerimento: Se vuoi convertire direttamente i numeri in parole, seleziona l'opzione Non convertito in Valuta e il risultato sarà mostrato così:
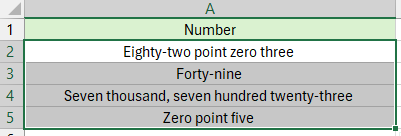
Quando Usare Ogni Metodo
Usa VBA se hai bisogno di una soluzione flessibile e programmabile e sei familiare con le macro.
- Usa LAMBDA se stai usando Excel 365 e devi convertire occasionalmente valori in Rupie Indiane. È una soluzione leggera e condivisibile che non richiede macro o strumenti esterni—perfetta per compiti semplici o personali.
- Usa Kutools per Excel se vuoi la soluzione più facile, veloce e versatile—nessuna codifica richiesta. Kutools è particolarmente utile quando:
- Devi gestire più valute.
- Hai bisogno di convertire valori in blocco o grandi dataset.
- Vuoi uno strumento pronto all'uso senza macro, professionale, con oltre 30 opzioni di valuta e prestazioni potenziate dall'IA.
I migliori strumenti per la produttività in Office
Potenzia le tue competenze in Excel con Kutools per Excel e sperimenta un'efficienza mai vista prima. Kutools per Excel offre oltre300 funzionalità avanzate per aumentare la produttività e farti risparmiare tempo. Clicca qui per ottenere la funzione di cui hai più bisogno...
Office Tab porta le schede su Office e rende il tuo lavoro molto più semplice
- Abilita la modifica e lettura a schede in Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Publisher, Access, Visio e Project.
- Apri e crea più documenti in nuove schede della stessa finestra invece che in nuove finestre.
- Aumenta la produttività del50% e riduce centinaia di clic del mouse ogni giorno!
Tutti gli add-in Kutools. Un solo programma di installazione
La suite Kutools for Office include add-in per Excel, Word, Outlook & PowerPoint più Office Tab Pro, ideale per i team che lavorano su più app di Office.
- Suite tutto-in-uno — Add-in per Excel, Word, Outlook & PowerPoint + Office Tab Pro
- Un solo programma di installazione, una sola licenza — configurazione in pochi minuti (pronto per MSI)
- Funzionano meglio insieme — produttività ottimizzata su tutte le app Office
- Prova completa30 giorni — nessuna registrazione, nessuna carta di credito
- Massimo risparmio — costa meno rispetto all’acquisto singolo degli add-in

